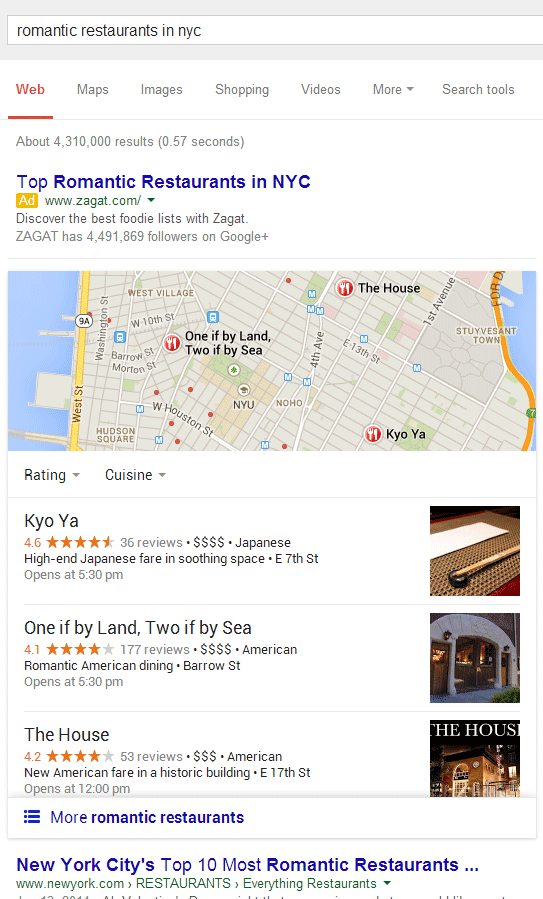
1. If you absolutely MUST use Java script drop down menus, image maps or image links, be sure to put text links somewhere on the page for the spiders to follow.
2. Content is king, so be sure to have good, well-written, and unique content that will focus on your primary keyword or keyword phrase.
3. If content is king, then links are queen. Build a network of quality backlinks. Remember, if there is no good, logical reason for a site to link to you, you don’t want the link.
4. Don’t be obsessed with PageRank. It is just one isty bitsy part of the ranking algorithm. A site with lower PR can actually outrank one with a higher PR.
5. Be sure you have a unique, keyword focused Title tag on every page of your site. And, if you MUST have the name of your company in it, put it at the end. Unless you are a household name, your business name will probably get few searches.
6. Fresh content can help improve your rankings. Add new, useful content to your pages on a regular basis. Content freshness adds relevancy to your site in the eyes of the search engines.
7. Be sure links to your site and within your site use your keyword phrase. In other words, if your target is “blue widgets” then link to “blue widgets” instead of a “Click here” link.
8. Focus on search phrases, not single keywords, and put your location in your text (“our Palm Springs store” not “our store”) to help you get found in local searches.
9. Don’t design your web site without considering SEO. Make sure your web designer understands your expectations for organic SEO. Doing a retrofit on your shiny new Flash-based site after it is built won’t cut it. Spiders can crawl text, not Flash or images.
10. Use keywords and keyword phrases appropriately in text links, image ALT attributes and even your domain name.
11. Check for canonicalization issues – www and non-www domains. Decide which you want to use and 301 redirect the other to it. In other words, if http://www.domain.com is your preference, then http://domain.com should redirect to it.
12. Check the link to your home page throughout your site. Is index.html appended to your domain name? If so, you’re splitting your links. Outside links go to http://www.domain.com and internal links go to http://www.domain.com/index.html.
Ditch the index.html or default.php or whatever the page is and always link back to your domain.
13. Frames, Flash and AJAX all share a common problem – you can’t link to a single page. It’s either all or nothing. Don’t use Frames at all and use Flash and AJAX sparingly for best SEO results.
14. Your URL file extension doesn’t matter. You can use .html, .htm, .asp, .php, etc. and it won’t make a difference as far as your SEO is concerned.
15. Got a new web site you want spidered? Submitting through Google’s regular submission form can take weeks. The quickest way to get your site spidered is by getting a link to it through another quality site.
16. If your site content doesn’t change often, your site needs a blog because search spiders like fresh text. Blog at least three time a week with good, fresh content to feed those little crawlers.
17. When link building, think quality, not quantity. One single, good, authoritative link can do a lot more for you than a dozen poor quality links, which can actually hurt you.
18. Search engines want natural language content. Don’t try to stuff your text with keywords. It won’t work. Search engines look at how many times a term is in your content and if it is abnormally high, will count this against you rather than for you.
19. Text around your links should also be related to your keywords. In other words, surround the link with descriptive text.
20. If you are on a shared server, do a blacklist check to be sure you’re not on a proxy with a spammer or banned site. Their negative notoriety could affect your own rankings.
21. Be aware that by using services that block domain ownership information when you register a domain, Google might see you as a potential spammer.
22. When optimizing your blog posts, optimize your post title tag independently from your blog title.
23. The bottom line in SEO is Text, Links, Popularity and Reputation.
24. Make sure your site is easy to use. This can influence your link building ability and popularity and, thus, your ranking.
25. Give link love, Get link love. Don’t be stingy with linking out. That will encourage others to link to you.
26. Search engines like unique content that is also quality content. There can be a difference between unique content and quality content. Make sure your content is both.
27. If you absolutely MUST have your main page as a splash page that is all Flash or one big image, place text and navigation links below the fold.
28. Some of your most valuable links might not appear in web sites at all but be in the form of e-mail communications such as newletters and zines.
29. You get NOTHING from paid links except a few clicks unless the links are embedded in body text and NOT obvious sponsored links.
30. Links from .edu domains are given nice weight by the search engines. Run a search for possible non-profit .edu sites that are looking for sponsors.
31. Give them something to talk about. Linkbaiting is simply good content.
32. Give each page a focus on a single keyword phrase. Don’t try to optimize the page for several keywords at once.
33. SEO is useless if you have a weak or non-existent call to action. Make sure your call to action is clear and present.
34. SEO is not a one-shot process. The search landscape changes daily, so expect to work on your optimization daily.
35. Cater to influential bloggers and authority sites who might link to you, your images, videos, podcasts, etc. or ask to reprint your content.
36. Get the owner or CEO blogging. It’s priceless! CEO influence on a blog is incredible as this is the VOICE of the company. Response from the owner to reader comments will cause your credibility to skyrocket!
37. Optimize the text in your RSS feed just like you should with your posts and web pages.Use descriptive, keyword rich text in your title and description.
38. Use keyword rich captions with your images.
39. Pay attention to the context surrounding your images. Images can rank based on text that surrounds them on the page. Pay attention to keyword text, headings, etc.
40. You’re better off letting your site pages be found naturally by the crawler. Good global navigation and linking will serve you much better than relying only on an XML Sitemap.
41. There are two ways to NOT see Google’s Personalized Search results:
(1) Log out of Google
(2) Append &pws=0 to the end of your search URL in the search bar
42. Links (especially deep links) from a high PageRank site are golden. High PR indicates high trust, so the back links will carry more weight.
43. Use absolute links. Not only will it make your on-site link navigation less prone to problems (like links to and from https pages), but if someone scrapes your content, you’ll get backlink juice out of it.
44. See if your hosting company offers “Sticky” forwarding when moving to a new domain.This allows temporary forwarding to the new domain from the old, retaining the new URL in the address bar so that users can gradually get used to the new URL.
45. Understand social marketing. It IS part of SEO. The more you understand about sites like Digg, Yelp, del.icio.us, Facebook, etc., the better you will be able to compete in search.
46. To get the best chance for your videos to be found by the crawlers, create a video sitemap and list it in your Google Webmaster Central account.
47. Videos that show up in Google blended search results don’t just come from YouTube. Be sure to submit your videos to other quality video sites like Metacafe, AOL, MSN and Yahoo to name a few.
48. Surround video content on your pages with keyword rich text. The search engines look at surrounding content to define the usefulness of the video for the query.
49. Use the words “image” or “picture” in your photo ALT descriptions and captions. A lot of searches are for a keyword plus one of those words.
50. Enable “Enhanced image search” in your Google Webmaster Central account. Images are a big part of the new blended search results, so allowing Google to find your photos will help your SEO efforts.
51. Add viral components to your web site or blog – reviews, sharing functions, ratings, visitor comments, etc.
52. Broaden your range of services to include video, podcasts, news, social content and so forth. SEO is not about 10 blue links anymore.
53. When considering a link purchase or exchange, check the cache date of the page where your link will be located in Google. Search for “cache:URL” where you substitute “URL” for the actual page. The newer the cache date the better. If the page isn’t there or the cache date is more than an month old, the page isn’t worth much.
54. If you have pages on your site that are very similar (you are concerned about duplicate content issues) and you want to be sure the correct one is included in the search engines,place the URL of your preferred page in your sitemaps.
55. Check your server headers. Search for “check server header” to find free online tools for this. You want to be sure your URLs report a “200 OK” status or “301 Moved Permanently ” for redirects. If the status shows anything else, check to be sure your URLs are set up properly and used consistently throughout your site.
Source: